test according to
UNE EN 62471
and IEC TR 62778





test according to
UNE EN 62471
and IEC TR 62778



ENAC photobiological safety tests according to UNE EN/IEC 62471 and IEC TR 62778
UNE EN/IEC 62471: evaluation of photobiological safety in lighting systems
The UNE EN/IEC 62471 standard presents a procedure to evaluate the photobiological safety of lamps and lamp systems, including luminair
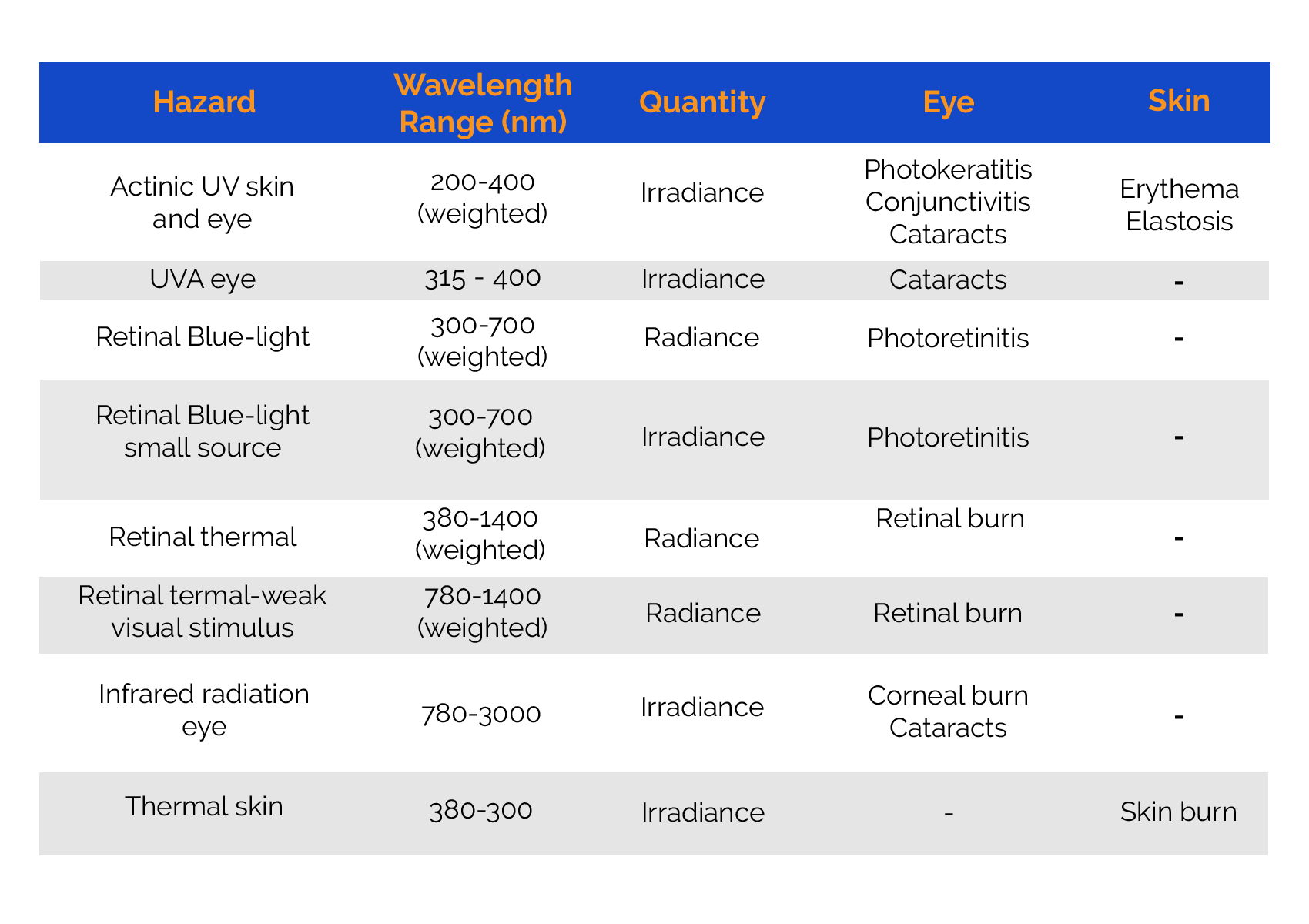
Specifically, it defines the exposure limits, technical measurement methods and the classification scheme for the evaluation and control of photobiological risks of all incoherent broadband sources of optical radiation, including LEDs.
The standard covers the wavelength range from 200 nm ultraviolet (UV) radiation to 3000 nm infrared (IR) radiation, including the 380nm-780nm visible (VIS) band.
Asselum’s radiometry laboratory has ENAC accreditation according to ISO 17025 for the performance of photobiological safety tests for the risks of near UV (UV-A) and blue light (LB, EB).
The UNE EN/IEC 62471 test method, on the photobiological safety of lamps and luminaires intended for general lighting services (GLS) applications, uses the GLS classification criteria of IEC 62471. That is, informing (but not necessarily measuring ) at a distance where the source produces an illuminance of 500 lux for GLS products and 200mm for Non-GLS equipment.
Once the measurement distance has been determined, 2 types of measurements are made depending on the risk to analyze according to IEC / UNE EN 62471. In addition, it defines two important radiometric parameters to evaluate the level of harmful radiation produced by a product. These are irradiance and radiance.
On the one hand, irradiance measures the total amount of radiation on an irradiated surface and assesses the risk of hazards to the skin and the front of the eye.
On the other hand, radiance measures the amount of radiation collected by the pupil and assesses the risk of dangers to the retina of the eye.
Once the effective irradiance and radiance values (irradiance and measured radiance multiplied by the hazard function) have been measured in the laboratory, they are compared to the limits defined in the standard.
Once the results have been compared with those defined in UNE EN/IEC 62471, the product is classified according to a level of potential risk for this product.
The IEC/UNE EN 62471 standard uses the following categories to report the level of risk:
Exempt Group
The philosophical basis for the exempt group classification is that the lamp does not represent any photobiological risk for the extreme points of this standard. This requirement is fulfilled by any lamp that does not represent:
- An actinic ultraviolet risk (Es) in 8h of exposure (30,000s); or
- a near UV risk (EUVA) in 1,000s, (around 16 min); or
- a retinal blue light (LB) risk in 10,000s (about 2.8); or
- a retinal thermal risk (LR) in 10s; or
- a risk to the eye from infrared radiation (EIR) in 1,000s.
Risk Group 1 – Low Risk
The philosophical basis for this classification is that the lamp does not pose a hazard due to normal operating limitations on exposure. This requirement is met by any lamp that exceeds the limits of the exempt group but does not represent:
- An actinic ultraviolet hazard (Es) in 10,000s; or
- a near ultraviolet hazard (EUVA) in 300s; or
- a retinal risk by blue light (LB) in 100s; or
- a retinal thermal risk (LR) in 10s; or
- a risk to the eye by infrared radiation (EIR) in 100s.
Risk Group 2 – Moderate Risk
The philosophical basis for the classification of risk group 2 (moderate risk) is that the lamp does not represent a hazard because of the aversion response to bright light sources or thermal distress. This requirement is met by any lamp that exceeds the limits of risk group 1 (low risk) but does not represent:
- An actinic ultraviolet hazard (Es) in 1,000s; or
- a near ultraviolet hazard (EUVA) in 100s; or
- a retinal risk due to blue light (LB) in 0.25s (aversion response); or
- a retinal thermal risk (LR) in 0.25s (aversion response); or
- a risk to the eye by infrared radiation (EIR) in 10s.
Risk Group 3 – High Risk
The philosophical basis for this classification is that the lamp does not represent a hazard even in a brief or momentary exposure. Lamps that exceed the limits of risk group 2 (moderate risk) are in risk group 3 (high risk).
This test procedure allows an analysis of the following photobiological hazards produced by an optical radiation source: